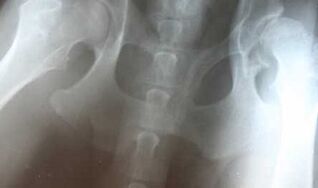
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a pathology that occupies a leading position among various degenerative-dystrophic problems of the musculoskeletal system. There are many reasons that provoke this disease, therefore, different age groups of people are at risk. It should be noted, however, that most often hip joint defeat occurs in middle-aged and elderly people.
Grade 1 hip osteoarthritis is successfully treated with medication without surgery. However, unfortunately, patients are in no hurry to consult a doctor immediately, mistakenly believing that the painful sensations will disappear on their own. In the meantime, the pathological process has already begun and is progressing more and more every day. Distinguish between primary arthrosis of the hip joints, which has an unclear and secondary etiology, resulting from such diseases:
- Perthes disease;
- congenital displacement;
- abnormal tissue development in the hip joint;
- aseptic necrosis of the femur;
- inflammatory processes;
- hip fractures.
One or two hip joints may be affected. Bilateral arthrosis is not uncommon, and with a unilateral pathological process may involve the spine and knee joints.
Causes of hip arthrosis
- deterioration of arterial blood flow and its venous flow, as a result of which the tissues are not nourished enough, there is an accumulation of sub-oxidized metabolic products that are responsible for the activation of enzymes;
- mechanical factors that cause joint overload, for example, overweight or occupational sports;
- biochemical changes in cartilage, hormonal disruptions, metabolic disorders;
- traumatic displacements, cervical and pelvic fractures;
- necrosis of the head tissue of the femur;
- inflammation of the joints, infectious processes;
- pathological changes in the spine (kyphosis, scoliosis) and flat feet;
- congenital femoral displacement;
- congenital pathologies of joint development;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary predisposition of the body (skeletal weakness, metabolic disorders, structural features of cartilage tissue).
The general symptoms of this pathological process are distinct, however, it should be understood that they can vary at different stages of osteoarthritis development. The main signs of hip joints are:
- pain in the groin, hip, joints and knee, which does not subside even in a relaxed state;
- stiffness and rigidity;
- çalim;
- femoral muscle atrophy;
- the affected limb becomes significantly shorter.
The main symptom of osteoarthritis of the hip joints is pain, intensity and duration, as well as the nature and localization of which depends entirely on the characteristics of the pathological process. It is best to start treatment at the onset of the illness, when the discomfort is not yet very pronounced. If proper measures are not taken in time, the pain will begin to intensify, as a result of which the mobility of the affected limb will be significantly limited.
Grade 2 hip osteoarthritis is characterized by severe radiating pain in the groin and thighs. In this case, the operation of the joint is disrupted, lameness appears, internal movement and hip abduction on the side are limited. The extensor and extensor muscles lose their strength, bone growths become visible on X-rays, which can come out strongly. The femoral head is deformed, its contour is distorted and the volume increases. In addition, cysts can form in the most stressed areas of the joint.
In stage 3 osteoarthritis, the pain becomes permanent and may even bother you at night. It becomes so difficult to walk that you have to use a special cane. At the hip joint, movements are limited, buttock muscles, atrophy of the thigh and lower leg affected, and the leg is shortened. All this leads to a change in gait and an increase in load on the affected joint. As a result of an increase in bone growth, the joint space disappears, and the joint grows together, eventually losing its mobility.
Treatment of hip arthrosis
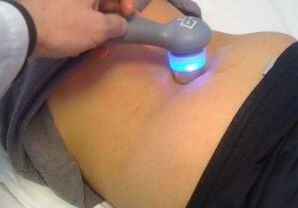
If the disease is detected at an early stage, preference is given to conservative methods of treatment, using different medications. The patient is mainly prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which perfectly relieve swelling and inflammation, due to which the pain syndrome is reduced. With muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at stimulating blood circulation and relieving spasms. In addition, for osteoarthritis, chondroprotectors are often used - medicines that allow the restoration of dilute cartilage tissue.
Do not forget about therapeutic massage and physiotherapy methods, as the effectiveness of such procedures is very high. Too often, they try to treat the affected joints with various compresses, lotions and oils prepared according to popular recipes, but all these remedies may not have the proper therapeutic effect. With their help, you can only temporarily relieve muscle pain and spasms. Before treating osteoarthritis of the hip joint, it is necessary to consult a doctor, as the independent use of one or another drug can only worsen an already complex condition.
Gymnastics for thigh arthrosis
Gymnastics plays an important role in treating the disease. Exercises specially selected for hip arthrosis prevent it from growing together and maintain movement. When developing an injured joint this way, you need to be very careful not to cause additional injury to yourself. Before performing exercise therapy exercises and immediately afterwards, it is recommended to perform muscle massage in the affected thigh and joint area to prevent the onset of discomfort.
Water is an excellent helper in the treatment of osteoarthritis, so it is helpful for the patient to swim in a pool, river or sea. In addition, a warm bath, in which you can perform smooth and slow movements of your feet, will help soothe pain and relieve muscle tension. It is important not to overload the injured joint and be at rest as much as possible.

















































